Research: New material biodegrades in ocean water
ANI
22 Sep 2022, 23:25 GMT+10

California [US], September 22 (ANI): Plastics, which are already pervasive in today's society, pose an increasing hazard to both human and environmental health. Evidence of plastic pollution can be found all over the world, from supermarket bags in the deep sea to tiny plastic particles in our food and even in our blood.
Scientists at the University of California, San Diego have created new biodegradable polymers that are intended to replace regularly used plastic in an effort to find answers to the growing problem of plastic litter. An interdisciplinary team of researchers led by UC San Diego biologist Stephen Mayfield and chemists Michael Burkart and Robert "Skip" Pomeroy has recently demonstrated that polyurethane foams dissolve in seawater after first demonstrating the material's biodegradation in land-based composts. The Science of the Total Environment journal publishes the findings.
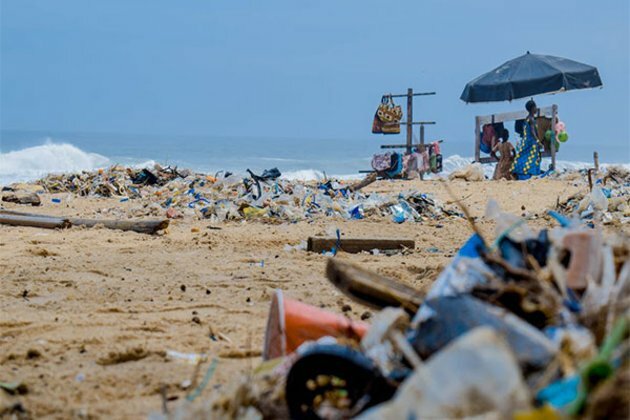
Scientists are attempting to address the plastic pollution issue, which is currently referred to as a global environmental calamity. In 2010, scientists expected that 8 billion kg of plastic would enter the ocean annually, and that number would sharply increase by 2025. Plastic trash disturbs marine ecosystems once it enters the water, moves to strategic areas, and forms trash gyres like the Great Pacific Garbage Patch, which has an extent of more than 1.6 million square kilometres. These plastics never break down; instead, they fragment into ever-tinier pieces that become microplastics, which linger in the environment for millennia.
The UC San Diego researchers tested their biodegradable polyurethane materials, which are currently used as foams in the first commercially available biodegradable shoes (sold by a spin-off company called Blueview), at Scripps' Ellen Browning Scripps Memorial Pier and Experimental Aquarium under the guidance of Samantha Clements, a marine biologist and scientific diver. The pier's position gave researchers access to and a one-of-a-kind chance to test materials in the ecology of the nearshore, which is the place where rogue plastics are most likely to end up.
"Improper disposal of plastic in the ocean breaks down into microplastics and has become an enormous environmental problem," said Mayfield, a professor in the School of Biological Sciences and director of the California Center for Algae Biotechnology. "We've shown that it's absolutely possible to make high performance plastic products that also can degrade in the ocean. Plastics should not be going into the ocean in the first place, but if they do, this material becomes food for microorganisms and not plastic trash and microplastics that harm aquatic life."Flip-flops, the most popular shoe in the world, and another footwear account for a sizable portion of the plastic trash dumped into landfills and oceans across the globe. The project gathered specialists in biology, polymer and synthetic chemistry, marine science, and other fields to thoroughly test and analyse the polyurethane materials, created at UC San Diego during the previous eight years. Foam samples were subjected to tidal and wave dynamics and chemical and physical changes were monitored using scanning electron microscopy and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy. The findings demonstrated that the material began to deteriorate as early as four weeks. The scientists then discovered microbes from six marine locations in San Diego that can degrade and consume the polyurethane substance.
No one academic subject can solve these pervasive environmental issues, but we have created an integrated approach that functions on land and, as we now know, also biodegrades in the ocean, according to Mayfield. "I was shocked to observe how many species live on these oceanic foams. It starts to resemble a microbial reef. (ANI) Share
Share
 Tweet
Tweet
 Share
Share
 Flip
Flip
 Email
Email
Watch latest videos
Subscribe and Follow
Get a daily dose of California Telegraph news through our daily email, its complimentary and keeps you fully up to date with world and business news as well.
News RELEASES
Publish news of your business, community or sports group, personnel appointments, major event and more by submitting a news release to California Telegraph.
More InformationInternational
SectionOver 60 companies named in UN report on Israel-Gaza conflict
GENEVA, Switzerland: A new United Nations report alleges that dozens of global corporations are profiting from and helping sustain...
UK lawmakers desigate protest group as terrorist organization
LONDON, UK - Lawmakers in the United Kingdom have voted overwhelmingly to proscribe the direct-action group Palestine Action as a terrorist...
Dalai Lama to address Buddhist conference, reveal succession plan
DHARAMSHALA, India: The Dalai Lama is set to address a significant three-day conference of Buddhist leaders this week, coinciding with...
US Supreme Court backs Texas efforts to shield minors online
WASHINGTON, D.C.: In a significant ruling last week, the U.S. Supreme Court upheld a Texas law requiring age verification for users...
Turkey, France battle wildfires amid early Europe heatwave
ISTANBUL/PARIS/BRUSSELS: As searing temperatures blanket much of Europe, wildfires are erupting and evacuation orders are being issued...
Venetians protest Bezos wedding with march through the town
VENICE, Italy: Over the weekend, hundreds of protesters marched through the narrow streets of Venice to voice their opposition to billionaire...
Business
SectionStandard and Poor's 500 and and Nasdaq Composite close at record highs
NEW YORK, New York -U.S. stock markets closed with broad gains on Thursday, led by strong performances in U.S. tech stocks, while European...
Persson family steps up H&M share purchases, sparks buyout talk
LONDON/STOCKHOLM: The Persson family is ramping up its investment in the H&M fashion empire, fueling renewed speculation about a potential...
L'Oreal to buy Color Wow, boosts premium haircare portfolio
PARIS, France: L'Oréal is making a fresh play in the booming premium haircare segment with a new acquisition. The French beauty conglomerate...
Robinhood launches stock tokens for EU investors, adds OpenAI
MENLO PARK, California: Robinhood is giving European investors a new way to tap into America's most prominent tech names — without...
Wall Street diverges, but techs advance Wednesday
NEW YORK, New York - U.S. stocks diverged on Wednesday for the second day in a row. The Standard and Poor's 500 hit a new all-time...
Greenback slides amid tax bill fears, trade deal uncertainty
NEW YORK CITY, New York: The U.S. dollar continues to lose ground, weighed down by growing concerns over Washington's fiscal outlook...